Mastering blindside waterproofing: A proactive, integrated approach
Better yet, sometimes the doubled-up members (or SOE braces in general) can be, with permission from the SOE designer and structural engineer, removed before the waterproofing installation. This practice eliminates the penetration altogether, which benefits the waterproofing performance.
Back-lagged soldier piles
While most soldier-pile-and-lagging SOE systems (which are prevalent in the mid-Atlantic where the authors are based) incorporate wood lagging at the building-side flange of the soldier pile (favorably creating a relatively planar substrate for the blindside waterproofing membrane), SOE designers sometimes elect to position the lagging outboard of the outer flange of the soldier pile (i.e. soil-side flange) in what is referred to as a “back-lagged” configuration. Other times, back-lagged piles may be the consequence of mis-driven or field-relocated piles to avoid a buried obstruction.
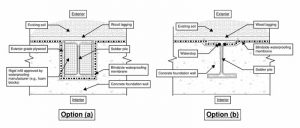
If back-lagging is necessary, the blindside waterproofing membrane must either: (a) contour around each soldier pile with additional details, such as infilling of the web space with rigid materials authorized by the waterproofing manufacturer, or (b) the waterproofing membrane must be interrupted at the web of each soldier pile. Both options (Figure 3) typically trigger complications requiring the structural engineer’s evaluation and may result in reinforcing bars needing to pass through each pile (possibly penetrating the waterproofing membrane) or the need to introduce structural pilasters to accommodate interruptions of foundation reinforcing. Option (a), especially if not captured by a coordinated design in the base bid, can be prone to change order requests to somewhat of a greater degree than option (b). Option (a), however, is significantly more reliable than option (b), which does not result in waterproofing membrane continuity and relies on sealants/mastics to terminate the waterproofing membrane at every pile flange, creating a waterproofing performance vulnerability at each back-lagged pile.
Geotechnical/environmental considerations
The project site’s subgrade and environmental characteristics, which are reported in a geotechnical report (and/or an accompanying environmental report), have fundamental relevance to blindside waterproofing design.
The geotechnical report typically incorporates a subsurface site investigation with soil borings and describes a recommended subgrade drainage strategy (if applicable). It suggests the design groundwater table elevation and describes the potential for fluctuating or perched groundwater.2 If the lowest floor level is near or below the groundwater table, the waterproofing and foundation must withstand hydrostatic conditions unless the site is permanently de-watered. Permanent subgrade dewatering systems may be feasible for certain circumstances,3 but they add perpetual operational costs and maintenance demands to the building. Such maintenance costs/demands can be significant and associated with the clearing of the under-slab drainage piping, construction and maintenance of emergency power generating systems, maintenance of sump pumps, and treatment of contaminated groundwater, if applicable. Many below-grade waterproofing manufacturers have enhanced details for waterproofing membranes when used in a hydrostatic versus non-hydrostatic condition.