Choosing the right door hardware with ANSI/BHMA standards
By Tony Gambrall

When specifying door hardware for a new or existing project, a lot of time and effort goes into ensuring every piece of hardware chosen will perform to its highest performance level. Seems simple, but every door opening has its own performance level and codes dictate this. How can specifiers ensure the door hardware chosen meets these differing levels? This is where the Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association (BHMA) and its door hardware standards can provide essential guidance.
BHMA is the trade association for North American manufacturers of commercial builders’ hardware and is involved in standards, codes and life safety regulations, and other activities that specifically impact builders’ hardware performance standards for locks, closers, exit devices, and other builders’ hardware.
BHMA is the only organization accredited by the America National Standards Institute (ANSI) to develop and maintain performance standards for locks, closers, exit devices, and other builders’ hardware. BHMA currently has more than 40 ANSI/BHMA standards. The widely known ANSI/BHMA A156 series of standards describes and establishes features and criteria for an array of builders’ hardware products including locks, closers, exit devices, butts, hinges, power-operated doors, and access control products.
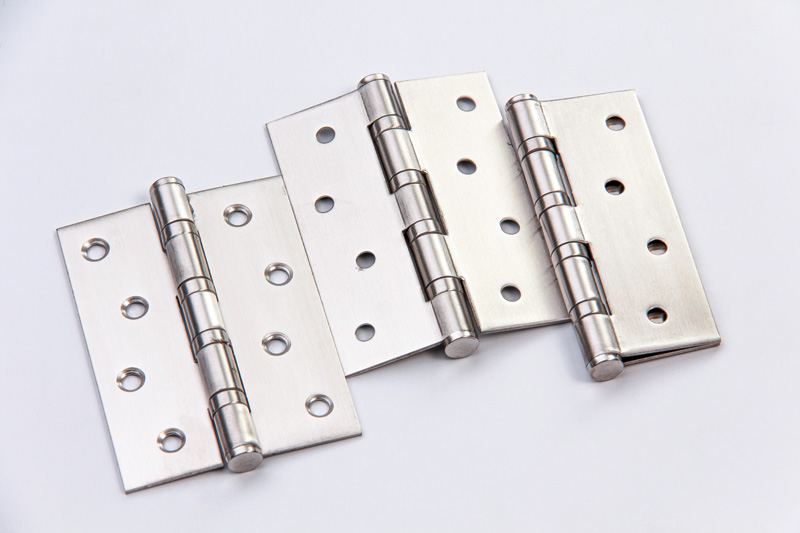

The different levels of ANSI grades
A typical BHMA standard is categorized according to the hardware’s intended use through the assignment of grades: 1, 2, and 3, with grade 1 representing the highest performance. Each grade is determined through a series of rigorous tests, which can include up to 15 to 20 different assessments. For instance, a grade 1 mortise lock must withstand 1,000,000 cycles in a cycle test, while grades 2 and 3 require 800,000 cycles. These strict laboratory tests are designed to guarantee that hardware exceeds these benchmarks in actual usage. Graded hardware aids in selecting the appropriate products, balancing performance and economic considerations.
Additionally, as the leader in commercial builders’ hardware, BHMA recognizes the requirements for residential products differ enough from those of commercial products to have separate standards. As a result, BHMA has developed two residential standards: one for deadbolts and another for locksets. These standards require that consumers be made aware of the three key areas in which these products have been tested, including security, durability, and finish.1

A deeper dive into ANSI/BHMA Standards
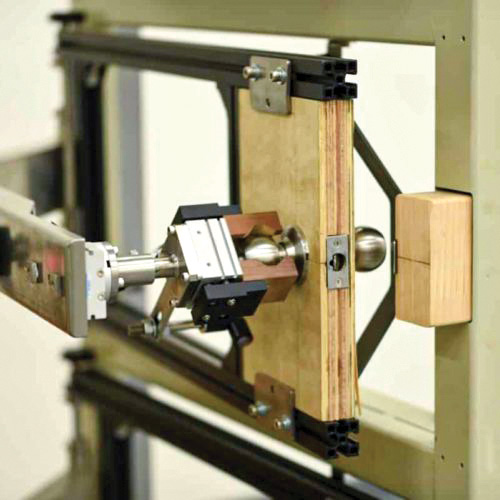
Let’s look at one of the standards: ANSI/BHMA, A156.1-2021 Butts and Hinges. This standard establishes requirements for butts and hinges. Cycle tests, lateral and vertical wear tests, friction tests, strength tests, finish tests, and material and dimensional requirements are included.

Material
The standard includes a table that lists the required steel gage and the number of fasteners for each standardized height. For example, a heavy-duty 127 mm (5 in.) hinge shall be made from steel gage 0.190 + .005 in and have four screw holes per mortised leaf.

Durability
Building products are expected to last a long time, and builders’ hardware is no exception. Grade 1 hinges, for example, must pass a rigorous test through 2.5 million cycles of opening and closing on a door of a specified weight.
Safety and security
Hinges may be specified with additional safety and security features for the application. The standard defines hospital hinges as having sloped barrels, maximum security pins (MSP), and non-removable pins (NRP), among others.
Appearance
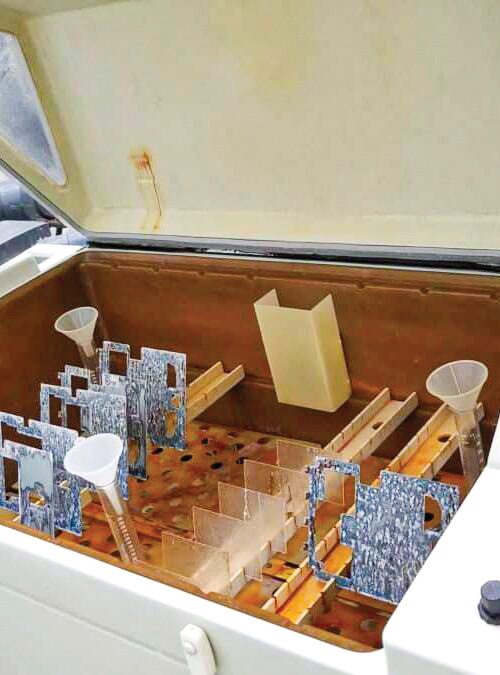
An additional duty of builders’ hardware is to be aesthetically attractive and stay that way. Corrosion resistance is evaluated through a salt spray test to ASTM B117 providing confidence in the ongoing appearance of the architectural metals and coatings.
Building codes
Builders’ hardware provides several attributes essential to building safety and performance, including egress and fire protection. BHMA hinges are designed to comply with all applicable requirements. For example, hinges which are acceptable for fire doors are described in NFPA 80.
Detention hinges
A section of the standard is dedicated to describing the requirements for detention hinges, including the test methods of ASTM F1758, Standard Test Methods for Detention Hinges Used on Detention-Grade Swinging Doors.
Sustainability
Locksets contribute to building sustainability through their verified durability, as well as material characteristics such as recycled content and recyclability. The reliable closing and sealing of openings can also contribute to energy conservation. BHMA has developed Product Category Rules, which will further define sustainability requirements and guide lifecycle assessments (LCAs) and environmental performance declarations (EPDs).
Type numbers
Another significant contribution of standards for product specification is a numbering system for hinge types. Please consult A156.1 for the full list; an example is provided here: A2412
- A—Section A
- 2—Material (wrought brass or bronze)
- 4—Type (half surface hinge)
- 1—Description (anti-friction bearing)
- 2—Grade (Grade 2)
Putting it together
Now, it is time to make the standard work for specifying a product. Using hinges again as the example, it is common knowledge that the opening requires the following hinges:
Stainless steel material, full mortise with frictionless bearings, and meets Grade 1 performance
From the A156.1 hinge standard, it is possible to put together an ANSI number of A5111. With that number, go to the BHMA Certified Product Directory1 and choose A156.1 as the standard. When the product page loads, enter A5111 in the “Click to show advanced search options” and products that meet the criteria will be displayed. As of today’s writing, 186 certified products have an ANSI number of A5111.
Certification of ANSI/BHMA standards
ANSI/BHMA A156 Series Standards are developed following accredited procedures. Stakeholders and other interested parties are welcome to provide their comments for consideration. BHMA standards are updated at least every five years; the project initiation and public review period are announced in ANSI Standards Action as required by the ANSI Essential Requirements.
Certification program
Participants in the BHMA Certification Program voluntarily submit a hardware product to independent laboratory testing to confirm the product fully meets the criteria of its ANSI/BHMA standard. In-factory audits are coordinated periodically to ensure the products comply with the standard. Products unable to pass the auditing process face loss of certification. This industry-wide certification program does not call for a manufacturer to be a BHMA member to certify its products.
ANSI/BHMA standards: Labeling compliance
Knowing the importance of using certified builders’ hardware is only part of what industry professionals and consumers need to know. It is equally crucial to understand how BHMA upholds the integrity of its certification program, ensuring that products tested to ANSI/BHMA standards can be trusted.
Notes
1 See buildershardware.com/Certification-Program/Certified-Products-Directory
Author
Tony Gambrall serves as the BHMA director of standards. He coordinates the development and revision of the BHMA performance standards for building hardware products. He came to BHMA following a career in door hardware manufacturing, focusing in the areas of product testing and development. During this time, Gambrall was also a BHMA member participating and chairing in the development of standards. He can be reached at agambrall@kellencompnay.com.
Key Takeaways
The Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association (BHMA) sets ANSI-accredited performance standards for commercial hardware like locks and exit devices. It uses graded classifications (1, 2, 3) based on rigorous testing to ensure durability, safety, and compliance with building codes. BHMA also provides residential standards and certification programs to verify hardware meets these requirements, helping specifiers choose suitable products for different building needs.