Next-gen sprayfoam systems: Shifting to HFO blowing agents

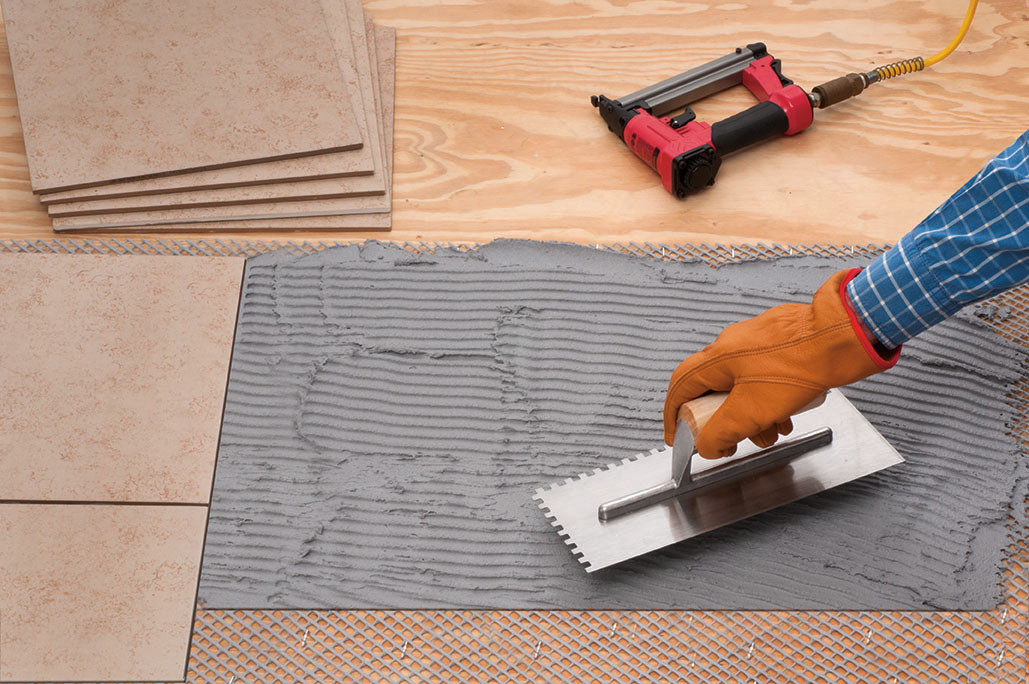
As a thermal insulator, closed cell SPF boasts one of the highest R-values per inch of all insulation options available. The material is ideal for continuous insulation (ci) applications in commercial structures and can be used in both interior and exterior applications where it can replace rigid extruded polystyrene (XPS), mineral wool, fiberglass, and polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam boards. The material
boasts low water absorption as well as resistance to mold, as demonstrated with ASTM C1338. Closed cell sprayfoam excels as a water-resistive barrier (WRB) on exterior wall applications and is tested in accordance with ASTM E2357, with a pressure up to 300 Pa (0.04 psi) for air barrier assemblies which included the ASTM E331 (AC71), Water Penetration Testing. The result was no leakage through the sprayfoam.
The air sealing capabilities of closed cell SPF insulation maintain indoor temperatures and reduce energy costs. They also improve indoor air quality (IAQ), minimizing the volume of allergens and pollutants able to enter the structure. Combined, these qualities result in an optimized building envelope, creating greater indoor comfort and reducing long-term heating and cooling demands.
When applied in walls, ceilings, and floors, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) names closed cell sprayfoam a Class 5 material, the highest classification for products indicating strong resistant to floodwater damage. Class 5 materials do not require special waterproofing protection, can survive wetting and drying and may be successfully cleaned after a flood to render them free of most harmful pollutants.2 While closed cell sprayfoam may be applied as cavity insulation or as continuous insulation in commercial structures and still qualify as a Class 5 material, it is the only cavity insulation approved by FEMA with this highest floodwater resistance. When applied under slab as insulation, closed cell sprayfoam is also flood and radon resistant.
The application of closed cell SPF in above grade walls can also increase the structural strength of buildings and assist with wind resistance. The degree of hardening depends primarily on the strength of the building. For example, an I-beam modular constructed metal building with a 22-gauge metal panel will benefit significantly less, regarding racking strength, from an interior application of closed cell SPF than a post-frame constructed building with 29-gauge corrugated metal panels. When installed, closed cell SPF essentially glues the assembly together, reduces the potential for movement, and adds a tensile strength average ranging from 103 to 172 kPa (15 to 25 psi).3
The Spray Polyurethane Foam Alliance (SPFA) conducted racking performance tests in 1992 and 1996 and at Architectural Testing Inc. in York, Pennsylvania in 2007. The tests demonstrated that medium density closed cell SPF, installed at 32 kg/m3 (2 lb/cf), increases racking strength by 70 to 200 percent in wall assemblies sheathed with oriented strand board (OSB), plywood, gypsum wallboard, vinyl siding, and polyiso board. The research proved closed cell SPF significantly increased rack and shear strength in both wood and metal construction. Installed SPF also increases the strength of weaker substrates such as gypsum drywall, vinyl siding, and polyiso foam insulation at a much greater percentage than stronger substrates such as OSB and plywood. Notably, special bracing for wind resistance is not required for strengthening purposes when using closed cell sprayfoam in walls.4
Sprayfoam roofing
One of the most rigid of all SPFs, sprayfoam roofing is applied to the top surface of low-slope roofs. In this application, the material acts as both a protective roofing material and as a thermal insulator. Like closed cell sprayfoam insulation, sprayfoam roofing is known for its air sealing capabilities and its energy efficiency. It is also the highest density sprayfoam as it must provide protection from moisture, rain, wind, hail, and other elements, as well as withstand maintenance-related foot traffic. The material offers a compressive strength of 714 to 1071 kg/m (40 to 60 lb/in.).